10 Unique Reagents that Helped Advance Research in 2019
As 2019 comes to an end, we like to look back and see how the reagents in our catalog have contributed toward scientific advances this past year. Our company mission is to facilitate access to unique reagents developed by academic laboratories. Together with our providing investigators, we work to take reagents sitting in laboratory freezers and make them available to scientists looking for those reagents around the world. Let’s look back at 10 of our reagents that were used in 2019 to further scientific research:
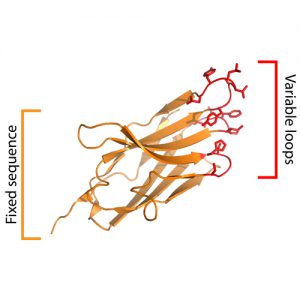
The Yeast-Display Nanobody Library, from Harvard University.
1. Yeast-Display Nanobody Library (NbLib)
From the laboratory of Andrew C. Kruse, PhD, Harvard University
The Yeast-Display Nanobody Library was added to our catalog in 2019 for nonprofit use. The reagent was originally cited in Nature and has been highly popular as it allows for rapid discovery of conformationally selective nanobodies. Nanobodies provide remarkable specificity for antibodies and the nanobody library has emerged as an especially useful tool in protein structural biology.
2. Burkitt Lymphoma Cell Lines
From the laboratory of Subhas C. Verma, PhD, University of Nevada, Reno
A new partnership between Kerafast and University of Nevada, Reno gave us the opportunity to offer two Burkitt Lymphoma cell lines from Dr. Verma. The available cell lines include a LANA-expressing Burkitt Lymphoma cell line and a control cell line, useful for studying the oncogenic potential of viral antigen in causing B-cell lymphoma. The University of Nevada, Reno released an article highlighting this new relationship.
3. Poly-ү-D-glutamic acid (PGA) [8B10] Antibody
From the laboratory of Thomas R. Kozel, PhD, University of Nevada, Reno
The same partnership between Kerafast and the University of Nevada, Reno opened the door for us to offer this poly-ү-D-glutamic acid antibody. The antibody can be used for the detection of Bacillus anthracis, an antigen associated with inhalational anthrax that is shed into blood and can be used to rapidly diagnosis the infection. Anthrax is a serious infectious disease and current biothreat.
4. ArborEasy DNA Isolation Kit
ArborEasy DNA Isolation Kit, from the Institute of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding.
From the laboratory of Modhumita Dasgupta, PhD, Institute of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding
Dr. Modhumita Dasgupta developed a non-biohazardous, low cost spin column-based system for isolating plant genomic DNA from a wide range of tissue types, specifically challenging tissues from tree species. This product was featured in an article in The Times of India highlighting the new relationship with Kerafast.
5. Cryptosporidium GP25-200/P23 Antibodies
From the laboratory of Michael W. Riggs, DVM, PhD, University of Arizona
Cryptosporidium parvum is an apicomplexan parasite that infects intestinal epithelium and causes diarrheal disease in humans, calves and other agriculturally important food animals worldwide. A panel of antibodies from the University of Arizona was developed for the better, faster diagnosis of Cryptosporidiosis. This new partnership and the release of the antibody panel was highlighted here.
From the laboratory of Scot R. Kimball, PhD, Penn State College of Medicine
The puromycin antibody provides a non-radioactive method to measure rates of global protein synthesis (mRNA translation), and it has proved useful across many research areas. This year alone, the antibody has been cited more than 25 times in peer-reviewed publications including mBio, Cell Death & Disease and Experimental Cell Research. Previously, a member from the Kimball Lab wrote a blog post for Kerafast that discusses using puromycin incorporation to measure global protein synthesis.
The MC-38 Cell Line, from the National Cancer Institute/NIH.
From the laboratories of James W. Hodge, PhD, MBA and Jeffrey Schlom, PhD, National Cancer Institute/NIH
The MC-38 cell line, derived from murine colon adenocarcinoma cells, was used for a variety of research applications in 2019. This year, our blog highlighted four papers citing the MC-38 cell line! Two of the papers were about CAR T-cell therapy, one about engineering nanobodies to make the therapy functional in solid tumors and the other about combating T cell exhaustion. The other two papers were about cancer spreading via hepatocytes and a new colon cancer therapeutic target. In our catalog, you can also find versions of the MC-38 cell line which have been engineered to express MUC-1 or carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
8. DNA-RNA Hybrid [S9.6] Antibody
From the laboratory of Stephen H. Leppla, PhD, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/NIH
Our DNA-RNA hybrid antibody continued to be used by researchers around the world, due to its high specificity and affinity for DNA-RNA hybrids and ability to detect R loops. In 2019 alone, we shipped the antibody to scientists on five different continents and saw it cited in peer-reviewed publications including Plant Cell, Molecular Biology Cell and PLoS One. Also, this year the antibody was cited in a publication we featured on our blog discussing how an HIV drug may reduce the impact of age-related disorders.
9. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV) Antibodies
From the laboratory of Douglas S. Lyles, PhD, Wake Forest School of Medicine
VSV is a widely used model system for studying viral replication and assembly, and the Lyles lab has made available various monoclonal antibodies that react with different epitopes in VSV’s G, M and N proteins. In 2019 alone, these antibodies were accessed and used by researchers across four different continents, with our team shipping to countries such as Spain, Germany, Australia, India and Israel. The procuring researchers were busy: we saw citations in publications including Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, Journal of Virology and Scientific Reports.
10. Integrin Beta 3 (GPIIIa, CD61), PSI Domain [AP-5] Antibody
From the laboratory of Richard H. Aster, MD, PhD, Blood Center of Wisconsin
Glycoprotein IIb/IIa is an integrin complex found on platelets which acts as a receptor for both fibrogen and von Willebrand factor and helps in platelet activation. This year the antibody was cited in a publication we featured in a blog post about a new target for anti-inflammation therapeutics. It was also used for research in various studies that were published in journals such as Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Nature Materials and Cell Death & Disease.


