Elderly Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease are More Susceptible to COVID-19 Infection
Researchers at the Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI) discovered elevated levels of ACE2 during SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor gene expression in elderly patients with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). The novel coronavirus (COVID-19), with its spread worldwide is reportedly hitting the elderly population most aggressively. Data has also shown that older people who have chronic comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have the highest mortality rate with this virus. The results of this study published in, Journal of Infection, concluded that extra precautions (healthcare provisions and diagnosis) should be taken for the elderly Alzheimer’s patients from COVID-19 as they are more vulnerable to the virus.
What is ACE2?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme attached to the cell membranes of cells in the lungs, arteries, heart, kidney and intestines. It also serves an entry point for some coronaviruses including the current pandemic strain SARS-CoV-2. ACE2 could be a potential therapeutic target to reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Expression in ACE2 gene is upregulated in elderly with Alzheimer’s Disease
KBRI’s research team looked at the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia through micro array data-set and total RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). The expression in brain tissue of the ACE2 gene, is elevated in the elderly with Alzheimer’s disease groups compared to the normal elderly (see figure). They also looked at ACE1 gene expression, but it did not differ in healthy vs. diseased brain tissue. Researchers also analyzed ACE2 gene expression levels in blood and found no significant differences. However, ACE1 gene expression was significantly increased in blood, concluding it may be a specific biomarker for AD diagnosis.
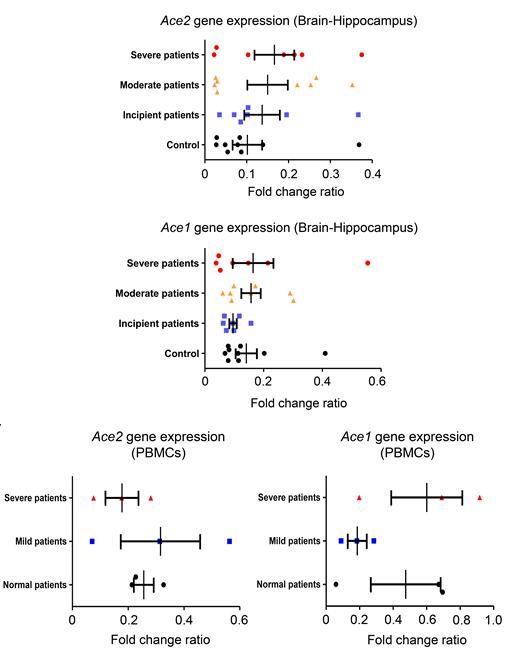
Analysis of Ace1 and Ace2 gene expression profile from human brain tissue and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Ace2 gene expression levels are elevated in the severe patient group compared to healthy group. Credit: Korea Brain Research Institute
The results suggest that high ACE2 expression may be a risk factor for Covid-19 transmission in AD patients. Researchers believe that finding treatments to reduce ACE2 expression could help both AD and COVID-19 patients in the elderly.
Related Research
Do you work in this field of research? If so, you may be interested in viewing our other reagents that might be related to COVID-19 or Alzheimer’s Disease research. Some of the reagents include:
- Coronavirus Reagents
- Alzheimer’s Disease Reagents
- Anti-Amyloid-beta [7H3D6] Antibody from University of Bonn
- Hyperphosphorylated Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau (MAPT) from Michigan State University
- Anti-SARS-CoV Spike Protein [S391] Antibody from National Jewish Health


